Inspirating Tips About How To Treat Iron Overload

Maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding alcohol, and reducing the amount of red meat and vitamin c in your diet are also recommended.
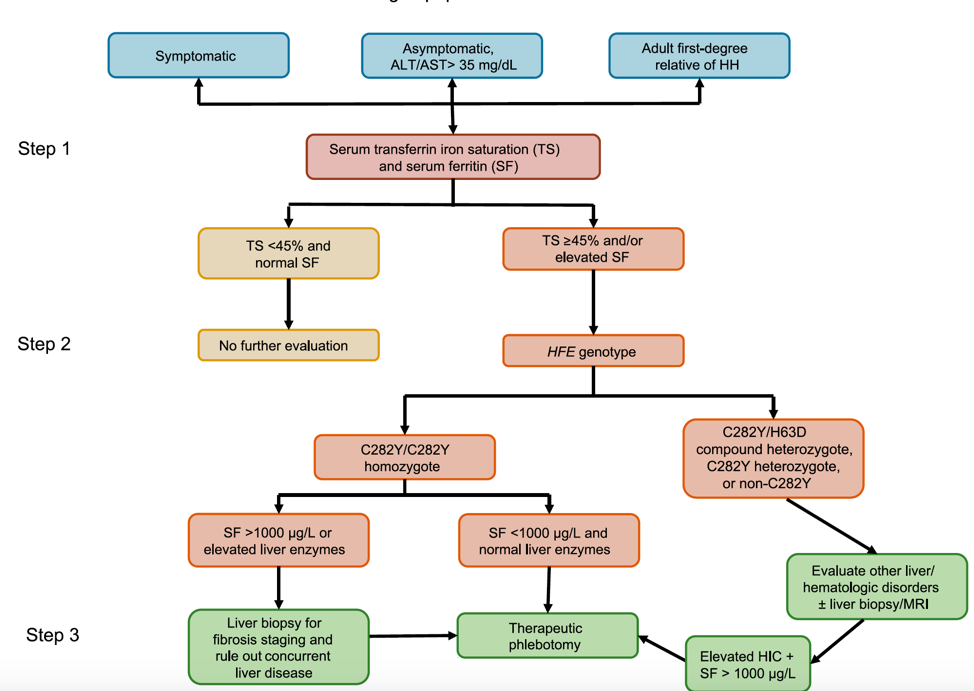
How to treat iron overload. Diagnosis is by elevated serum ferritin, iron, and transferrin saturation levels. Maintenance therapy is adjusted to prevent tissue damage because of iron overload. There are a few types of hemochromatosis, but the most common type is caused by a gene change passed down through families.
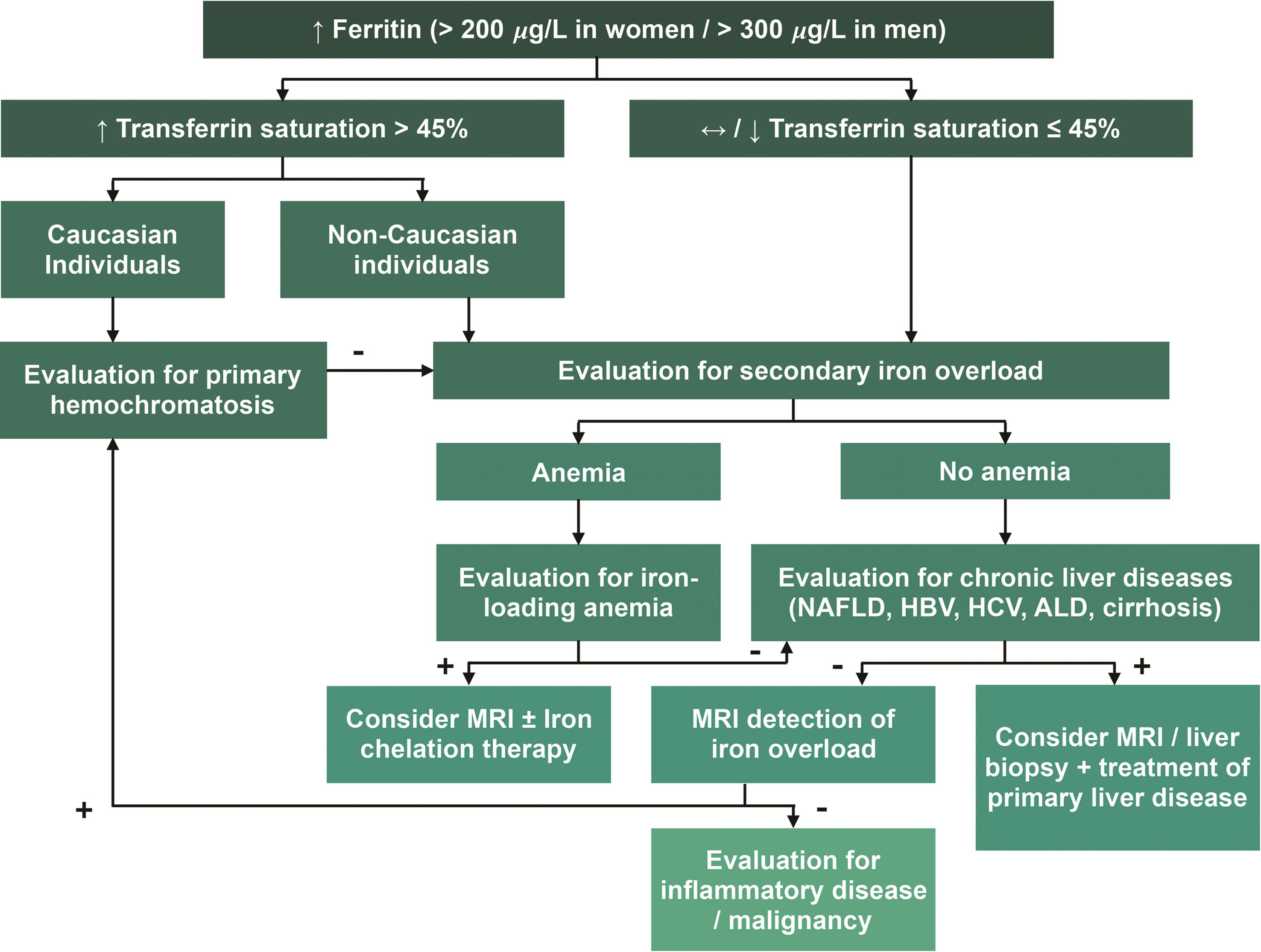
(see also overview of iron overload.) Diagnose by measuring serum ferritin level; Haemochromatosis is an inherited condition where iron levels in the body slowly build up over many years.
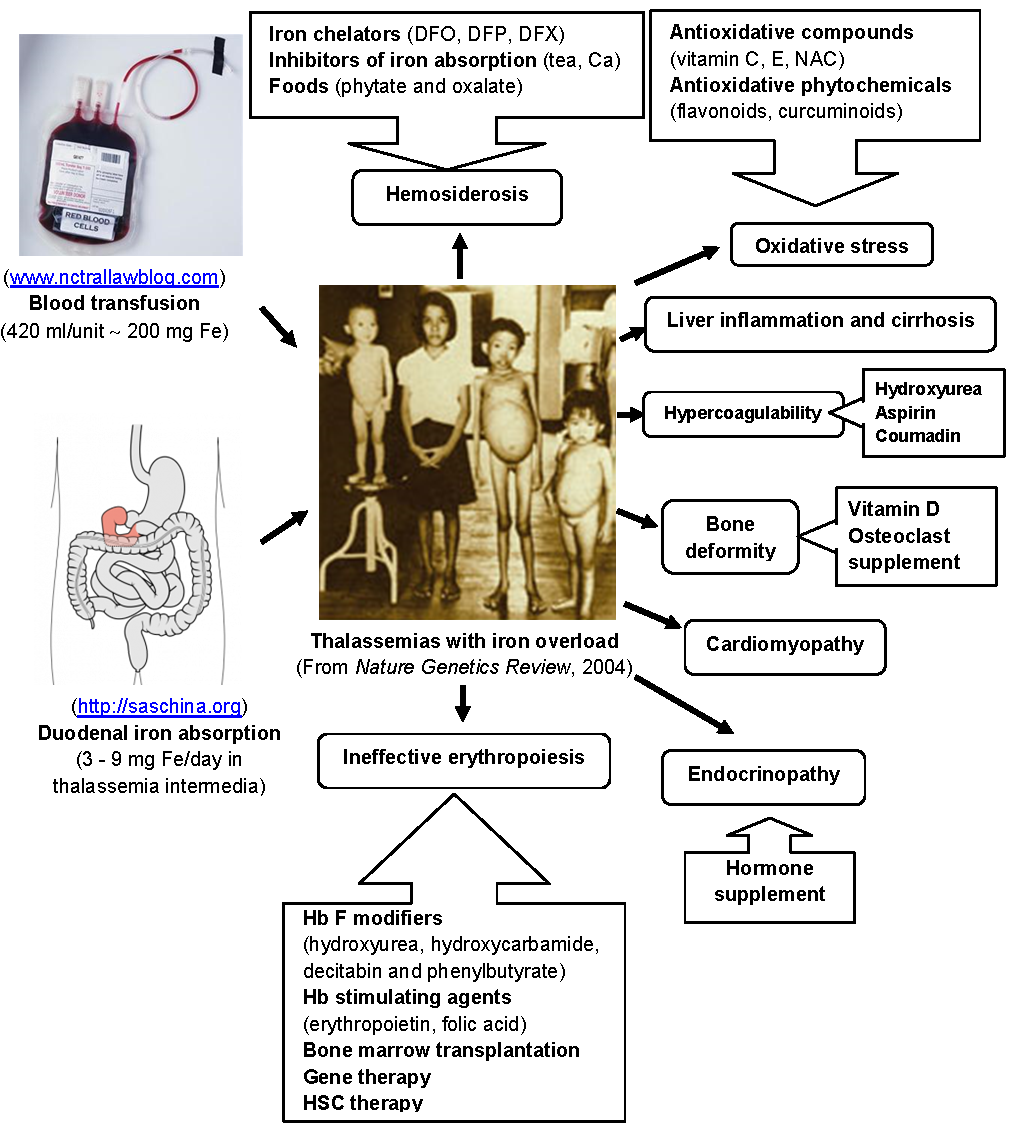
Treatment eating, diet, & nutrition treatment of hemochromatosis how do doctors treat hemochromatosis? Iron overload is treated with chelation. If it is not treated, this can damage parts of the body such as the liver, joints, pancreas and heart.
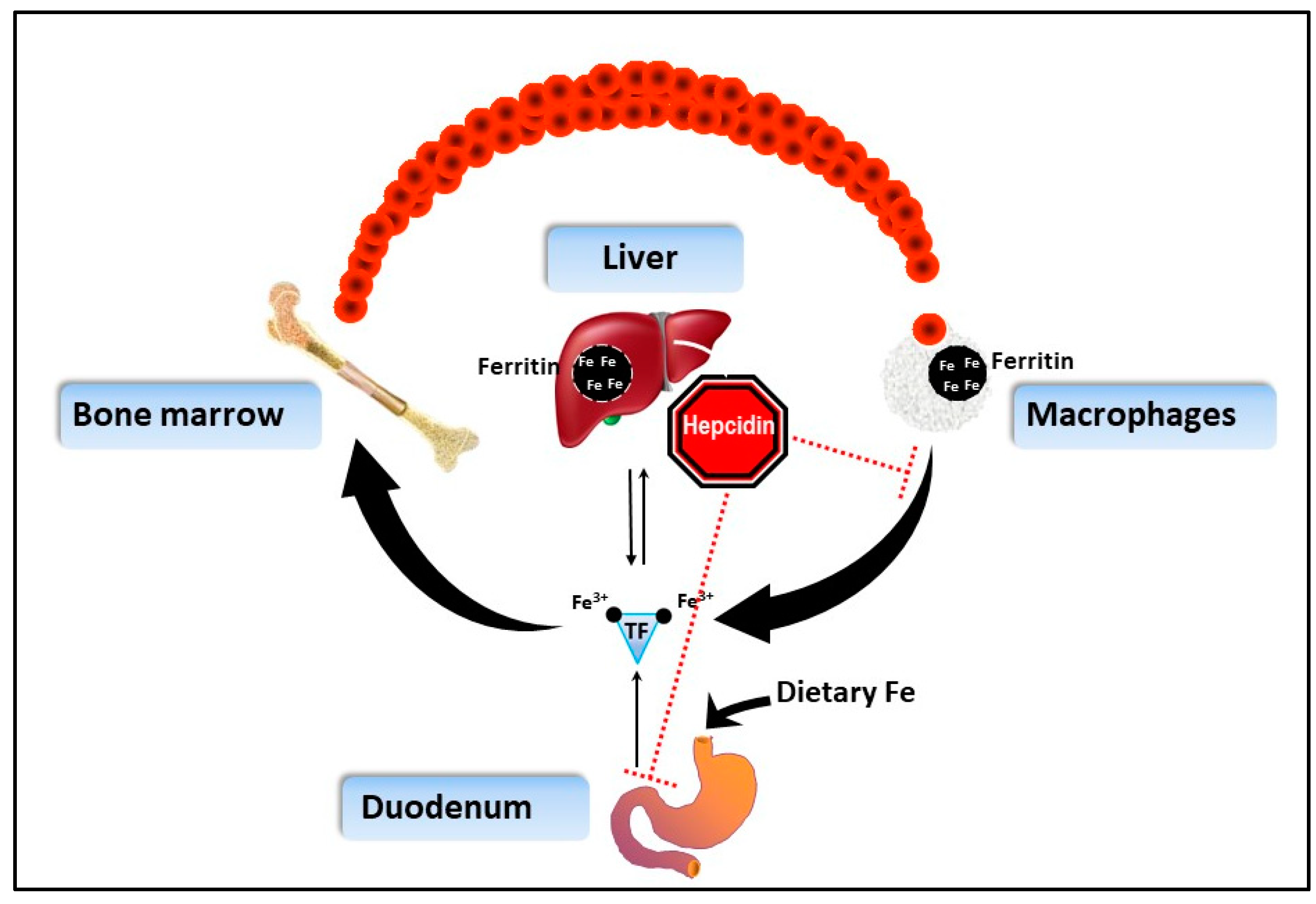
Introduction iron is an essential element and plays a critical role in various metabolic processes in the body, including oxygen transport, energy production, and immune response. 6 besides being a crucial component of hemoglobin with a key role in erythropoiesis, oxygen transportation and storage, iron also has further important functions as part of. [1] in certain disease states, an excess of iron can accumulate in the body.
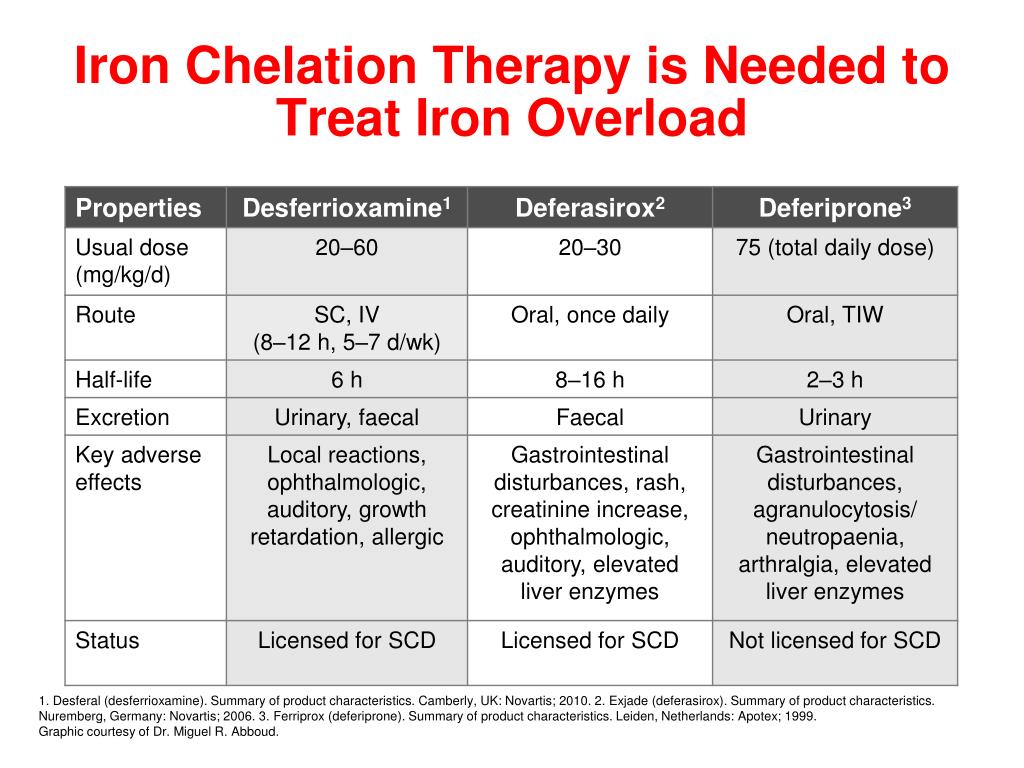
If cardiac iron overload is present (t2* < 20 ms), cardiac iron removal becomes the primary goal of therapy. Avoid raw or undercooked fish and shellfish. Goals of iron chelation therapy.
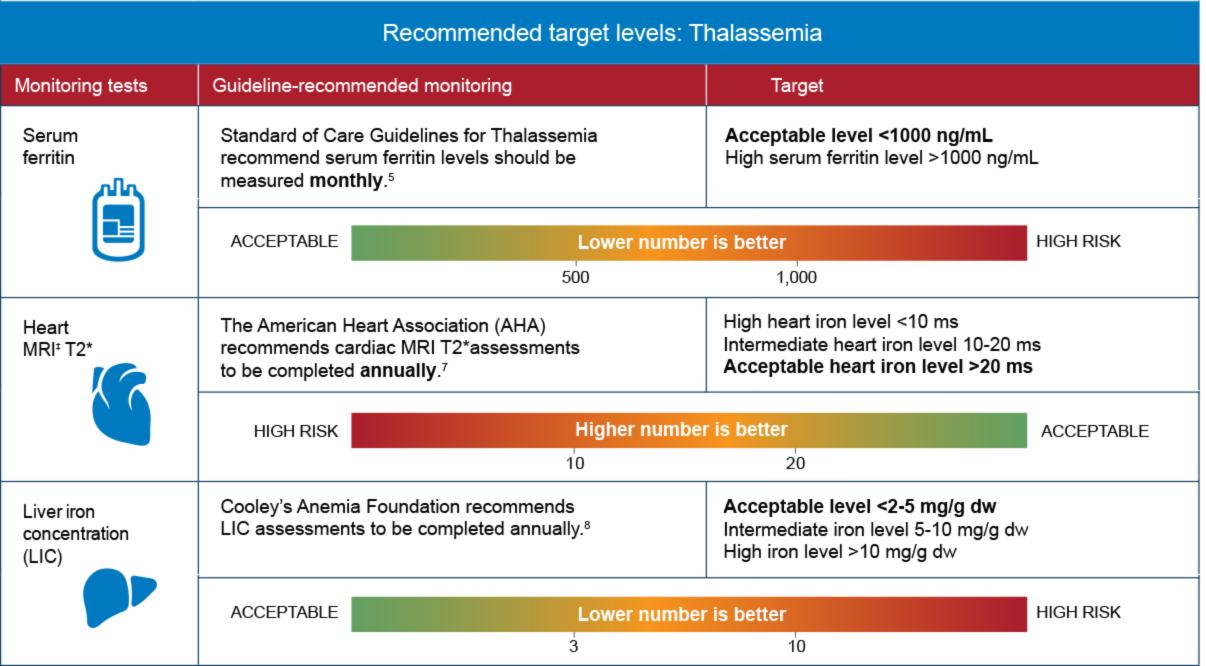
Serial monitoring of iron stores can prevent iron overload in patients on chronic transfusion therapy. If elevated, confirm by demonstrating elevated serum iron and transferrin saturation. Hemochromatosis, iron, phlebotomy, iron overload, diet.
Iron chelation therapy uses medications that bind, or chelate, iron and facilitate its removal. There are various different methods for evaluating iron overload degree including serum ferritin levels, liver iron concentration determined from biopsy, superconducting quantum interference device (squid) and. Despite the significant morbidity associated with iron overload ( ballas 2001) it remains difficult to distinguish whether organ damage in scd is a consequence of iron from transfusions used to treat scd complications or due to the complications themselves.
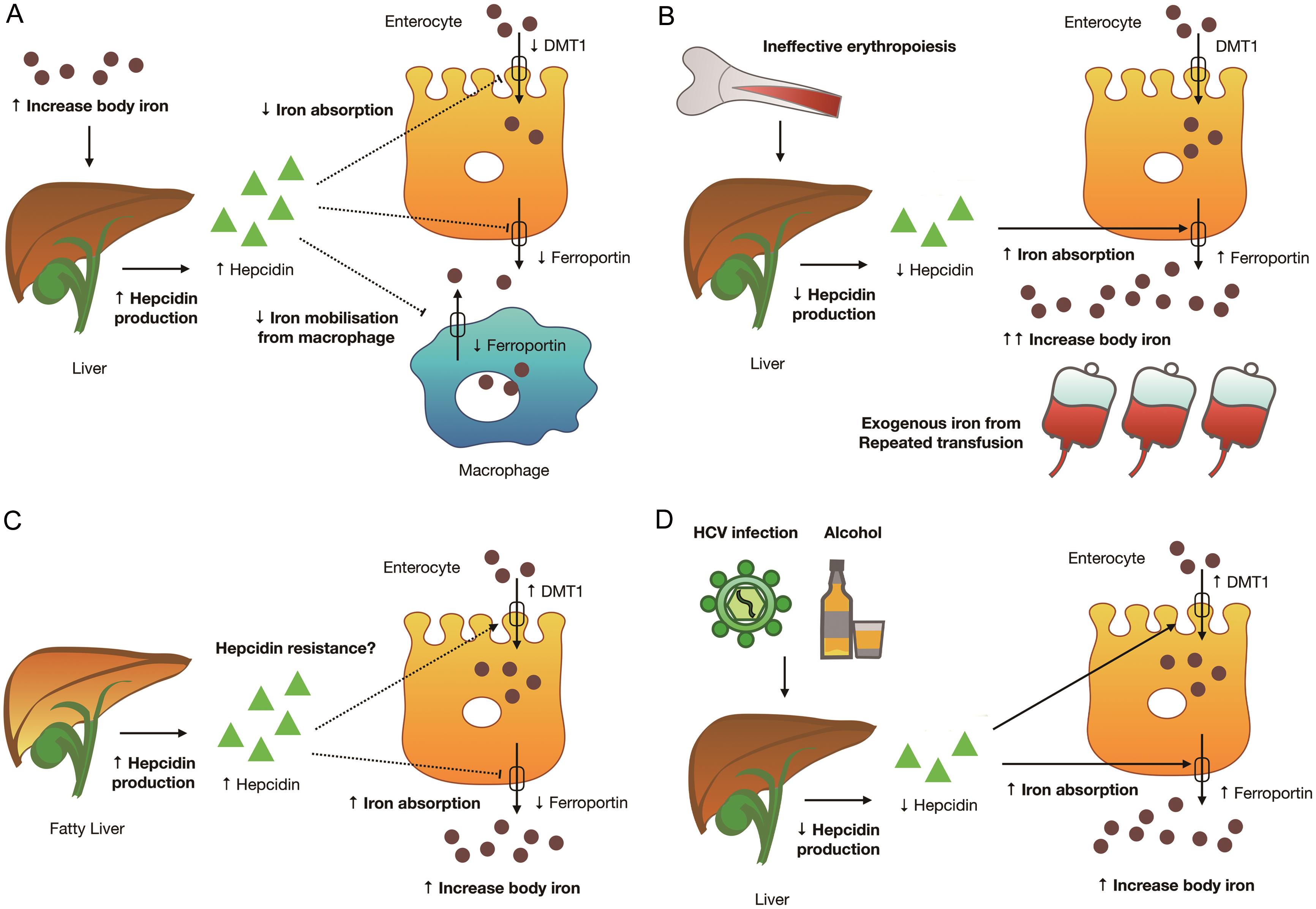
Management of the anemia may require repeated transfusions. Iron overload may result from hereditary hemochromatosis (a genetic disorder of iron metabolism) or from secondary hemochromatosis , an acquired form of the disease that is due to excess oral intake or absorption of iron or to repeated blood transfusions ( 1, 2 ). Iron overload is the accumulation of excess body iron in different organs as a result of increased intestinal absorption, parenteral administration, or increased dietary intake.
This article discusses how to eat on the hemochromatosis diet. In the beginning, you may have a pint (about 470 milliliters) of blood taken once or twice a week — usually in a hospital or your provider's office. The primary treatment is weekly blood removal to lower iron stores.
36,91,92 a lic > 15 mg/g dry weight, serum ferritin > 2500 μg/l or cardiac t2* mri < 20 ms indicate inadequate chelation. The amount of blood removed and how often it's removed depend on your age, your overall health and the severity of iron overload. The diagnosis is made on the basis of the characteristic erythroblast morphology.